
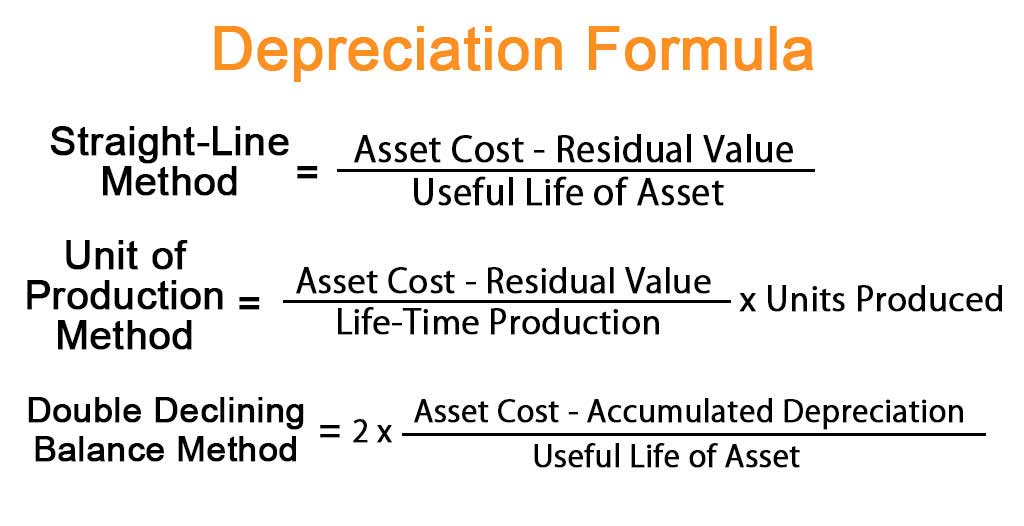
Regardless of these conceptual arguments, a company’s managers can choose between these accelerated depreciation methods for any depreciable asset. Depreciation expense for the remaining three years is calculated in a similar way. Both the declining balance and sum-of-the-years’ digits methods are examples of accelerated depreciation. Sum-of-the-years’ digits is a method that uses an arbitrary arithmetic system to derive the annual depreciation charges. Based on the depreciation expense calculated for each year of the asset’s life in Step 4, calculate the depreciation amount that needs to be charged for each accounting period. Depreciation is a method of asset cost allocation that apportions an asset’s cost to expenses for each period expected to benefit from using the asset.
Do you own a business?
This rate is a fraction, in which the numerator is the number of years remaining in the asset’s life at the beginning of the year and the denominator is the sum of the digits of the asset’s useful life. Note that the asset’s residual value is subtracted from its acquisition cost to determine its depreciable base. In this method, you multiply the depreciable basis amount by an annual fraction. The denominator is the sum of the digits from 1 to n, where n is the number of years in the asset’s service life. We need to deduct the salvage value ($2000) from the initial cost ($12000) to calculate the delivery truck’s depreciation base.
Sum of Years Depreciation Calculator Instructions
For example, if an asset costs $1000 and has a salvage value of $200, its depreciation base is $800. For example, if an asset has a useful life of 5 years, the sum of its years’ digits will equal 15 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
Step 4
The company can calculate sum of the years’ digits depreciation after determining the expected useful life of the fixed asset and the depreciable cost to use as a basis of calculation. The remaining useful life of the fixed asset is determined separately in each year of depreciation in the sum of years’ digits depreciation methods. For example, if the fixed asset has 5 years of useful life, the remaining useful life on the first-year calculation of depreciation is 5 while the last year or fifth year will be 1. Sum of the years’ digits depreciation uses the assumption that the benefits that the company receives from the fixed asset will go down through the passage of time. It is similar to the declining balance depreciation in which the depreciation expense in the sum of the years’ digits method will go down as time passes making the last depreciation expense the smallest. An accelerated depreciation method, the double-declining method calculates depreciation twice as fast as that in the declining balance method.
Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits: Definition
In other words, the difference is in the timing of when the same total amount of depreciation will be reported. Sum of the years’ digits depreciation method, like reducing balance method, is a type of accelerated depreciation technique that allocates higher depreciation expense in the earlier years of an asset’s useful life. Where an entity has a policy of calculating depreciation on full years basis, sum of the years’ digits depreciation can be calculated as above. Assets that lose their value the most in the beginning usually require less maintenance in the beginning and more maintenance in the later years. As such, with the accelerated methods of depreciation, companies account for higher depreciation expenses in the beginning and less maintenance costs. Towards the end of the asset’s life, there will be less depreciation expenses since most have been depreciated in the beginning but there will be a lot more maintenance costs to keep the asset running.
- Depreciation charges for the first two years of the asset are $45,000 and $30,000 respectively (refer the solution of the example above in case of confusion).
- For the calculation, you will need to know the total useful life of the asset.
- With Deskera CRM you can manage contact and deal management, sales pipelines, email campaigns, customer support, etc.
- Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
- Enter the period for which you want the sum of the years digits depreciation expense.
- However, the depreciation expense in the sum of the years’ digits goes down in the linear line instead of the curve line like those in the declining balance method.
Advantages of the SYD Method
Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
The sum-of-the-years’ digits method is another variation on accelerated depreciation. Under this method, an asset’s depreciable base is multiplied by a declining rate. Calculate the sum of years’ digits depreciation for each year of the fixed asset above.
The total acquisition cost refers to the total capital expenditure that the company had to undertake in order to gain possession of said assets. The sum of years’ method matches the cost of utilizing an asset and the overall utility of the asset across the economic or useful life of the asset. A major benefit of using this method is that it considers the fact that the asset performance will decline over the years; i.e. the asset is more productive in the early years. Therefore, it is only apt to charge a higher depreciation in the early years and decrease it in later years. It calculates depreciation expenses based on the number of years of the useful life of an asset. While it involves more complex calculations and may impact financial statements differently than other methods, its benefits in terms of tax efficiency and cash flow management make it a compelling choice for many businesses.
Depending on the chosen cost apportionment or depreciation rate, depreciation charges can be variable, straight-lined, or accelerated over the useful life of an asset. The final step is to allocate this total depreciation to each of the years of its useful life in proportion to the remaining life of the asset at the beginning of the year using the sum of the years digits depreciation formula. Depreciation is the process cash receipt templates of the allocation of fixed assets cost over their useful life. However, the company needs to properly allocate the cost so that the depreciation expense charged to the income statement matches the benefits that the company receives from the fixed assets. This is so that the recognition of the depreciation expense in the company’s account is properly in compliance with the matching principle of accounting.
